API Mediation Layer routing
API Mediation Layer routing
As an application developer, you can route your service through the Gateway using the API Mediation Layer to consume a specific resource.
There are two ways to route your service to the API Mediation Layer:
- Basic Routing (using Service ID and version)
- Basic Routing (using only the service ID)
Terminology#
Service
A service provides one or more APIs, and is identified by a service ID. Note that sometimes the term "service name" is used to mean service ID.
The default service ID is provided by the service developer in the service configuration file.
A system administrator can replace the service ID with a deployment environment specific name using additional configuration that is external to the service deployment unit. Most often, this is configured in a JAR or WAR file.
Services are deployed using one or more service instances, which share the same service ID and implementation.
URI (Uniform Resource Identifier)
A string of characters used to identify a resource. Each URI must point to a single corresponding resource that does not require any additional information, such as HTTP headers.
APIML Basic Routing (using Service ID and version)#
This method of basic routing is based on the service ID that identifies the service. The specific instance is selected by the API Gateway. All instances require an identical response. Eureka and Zuul expect this type of routing.
The URI identifies the resource, but does not identify the instance of the service as unique when multiple instances of the same service are provided. For example, when a service is running in high-availability (HA) mode.
Services of the same product that provide different resources, such as SYSVIEW on one system and SYSVIEW in a different sysplex, cannot have the same service ID (the same URI cannot have two different meanings).
In addition to the basic Zuul routing, the Zowe API Gateway supports versioning in which you can specify a major version. The Gateway routes a request only to an instance that provides the specified major version of the API.
The /api/ prefix is used for REST APIs. The prefix /ui/ applies to web UIs and the prefix /ws/ applies to WebSockets.
You can implement additional routing using a Zuul pre-filter. For more information about how to implement a Zuul filter, see Router and Filter: Zuul
The URL format expected by the API Gateway is:
https://{gatewayHost}:{port}/{serviceId}/api/v{majorVersion}/{resource}
Example:
The following address shows the original URL of a resource exposed by a service:
http://service:10015/enablerv1sampleapp/api/v1/samplesThe following address shows the API Gateway URL of the resource:
https://gateway:10010/enablerv1sampleapp/api/v1/samplesThe following diagram illustrates how basic routing works:
Implementation Details#
Service instances provide information about routing to the API Gateway via Eureka metadata.
Example:
metadata-map: apiml: routes: ui_v1: gatewayUrl: "ui/v1" serviceUrl: "/helloworld" api_v1: gatewayUrl: "api/v1" serviceUrl: "/helloworld/v1" api_v2: gatewayUrl: "api/v2" serviceUrl: "/helloworld/v2"In this example, the service has a service ID of helloworldservice that exposes the following endpoints:
- UI -
https://gateway/helloworldservice/ui/v1routed tohttps://hwServiceHost:port/helloworld/ - API major version 1 -
https://gateway/helloworldservice/api/v1routed tohttps://hwServiceHost:port/helloworld/v1 - API major version 2 -
https://gateway/helloworldservice/api/v2routed tohttps://hwServiceHost:port/helloworld/v2
where:
- The gatewayUrl is matched against the prefix of the URL path used at the Gateway
https://gateway/urlPath, whereurlPathisserviceId/prefix/resourcePath. - The service ID is used to find the service host and port.
- The
serviceUrlis used to prefix theresourcePathat the service host.
Note: The service ID is not included in the routing metadata, but the service ID is in the basic Eureka metadata.
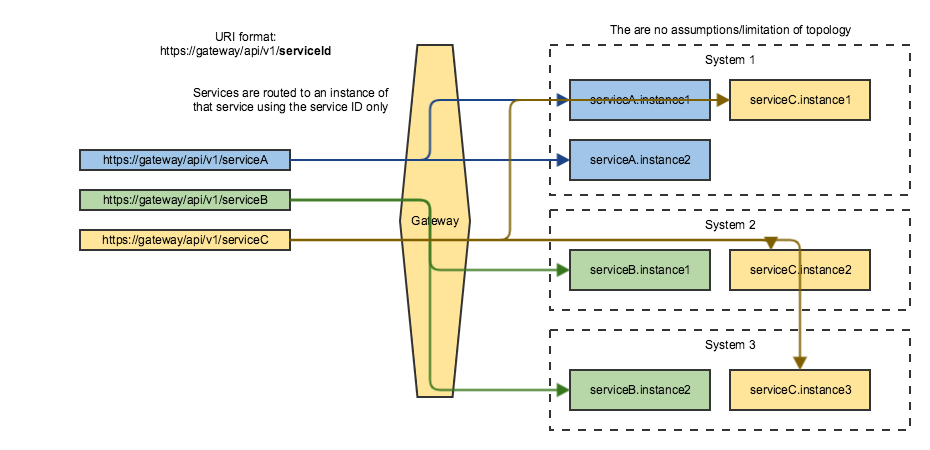
Basic Routing (using only the service ID)#
This method of routing is similar to the previous method, but does not use the version part of the URL. This approach is useful for services that handle versioning themselves with different granularity.
One example that only uses a service ID is z/OSMF.
Example:
z/OSMF URL through the Gateway: https://gateway:10010/zosmf/api/restjobs/jobs/...
where:
zosmfis the service ID./restjobs/1.0/...is the rest of the endpoint segment.
Note that no version is specified in this URL.